
Once the gdebi tool is installed, you can easily install deb files. You will have to install it manually using the command “sudo apt install gdebi”. You must know that the gdebi package manager is not installed by default in Ubuntu. It can also resolve build-depends of debian/control files. Note that the apt tool does the same, but only for remote (http, ftp) located packages. gdebi lets you install local deb packages resolving and installing its dependencies. The gdebi is a simple tool to install deb files. Terminal Method using GDEBI Package Manager You can the run the following commands to install deb package using apt: The apt is the default package manager and is one of the easiest ways to install a deb package.

In such case, run the following command to install the pending dependencies alongwith the deb package: In some cases you may get dependency error while installing the deb package. The sudo apt-get install -f command tries to fix this broken package by installing the missing dependency.Run the following command to install deb package: When dpkg installs a package and a package dependency is not satisfied, it leaves the package in an "unconfigured" state and that package is considered broken. Why use sudo apt-get install -f after sudo dpkg -i /path/to/deb/file (as mentioned in method 1)?įix attempt to correct a system with broken dependencies in place. All these methods will fail to satisfy the software dependency if the dependencies required by the deb is not present in the package index.
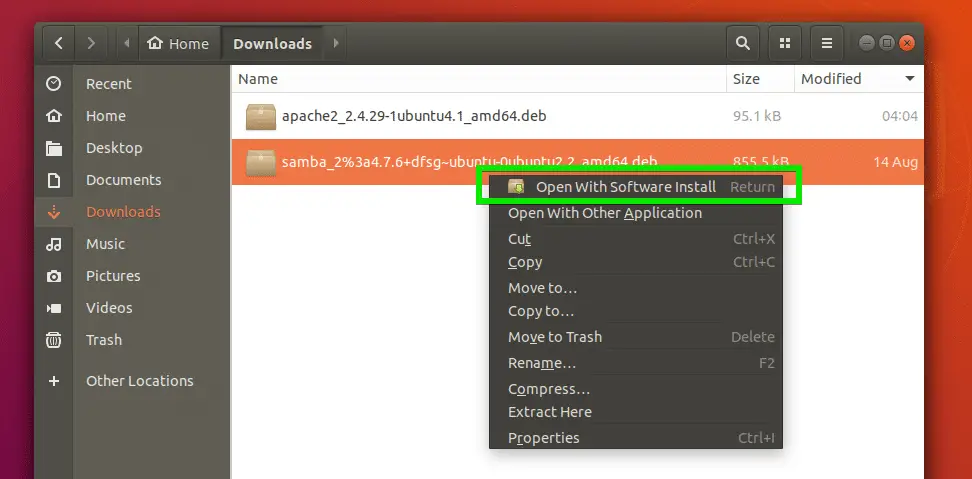
Note: APT maintains the package index which is a database ( /var/cache/apt/*.bin) of available packages available in repo defined in /etc/apt/sources.list file and in the /etc/apt/ directory. deb file using it ( Right-click -> Open with). For both, after executing this command, it will automatically download its dependencies.įirst installing gdebi and then opening your. With old apt-get versions you must first move your deb file to Once the download is finished it calls dpkg to install all those files, satisfying all the dependencies. When you install a package using apt, it first creates a list of all the dependencies and downloads it from the repository. When you use apt to install a package, under the hood it uses dpkg.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
